After losing touch for a week, NASA hears the Voyager 2 probe's heartbeat signal
After losing touch for a week, NASA hears the Voyager 2 probe's heartbeat signal.
Voyager 2: A Journey Through the Cosmic Frontier
On Aug. 1, NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) Twitter account confirmed that engineers had received a transmission called a carrier signal from Voyager 2 — which is currently cruising beyond the edge of the solar system more than 12.3 billion miles (19.9 billion kilometers) from Earth.
"A bit like hearing the spacecraft's 'heartbeat,' it confirms the spacecraft is still broadcasting, which engineers expected," JPL officials tweeted.
● Right now, where is Voyager 2?
● Has Voyager 2 survived?
In order to keep Voyager 2 operational until at least 2026, NASA is using backup power. NASA's Voyager spacecraft as depicted by an artist. Their power supplies are gradually deteriorating since the 1977 launches of Voyager 1 and its copy Voyager 2.
Introduction:
With its incredible journey through space, Voyager 2, one of NASA's most famous space projects, has captured the attention of people all over the world. The spacecraft, which was launched on August 20, 1977, a few weeks before its companion Voyager 1, has given us priceless knowledge about the solar system and beyond. We will explore the intriguing history, accomplishments, and discoveries made by Voyager 2 as it journeyed into the uncharted regions of space in this blog.
Early Missions and Launch:
A Titan IIIE/Centaur rocket carrying Voyager 2 was fired from Cape Canaveral, Florida. The project was created to take advantage of a unique planetary alignment that allowed both spacecraft to study a number of gas giants in addition to the flybys of Jupiter and Saturn, which were the original goals of the mission. Voyager 2 subsequently began a massive tour of the outer planets, an extraordinary achievement in space research.
Grand Tour:
The Grand Tour of Voyager 2 began on July 9, 1979, when it made its first contact with Jupiter. Beautiful photographs of the planet and its moons were taken by the spacecraft, which revealed the complex intricacies of Jupiter's cloud bands and the raging volcanic activity on its moon Io. This encounter helped to prepare Voyager 2 for its flyby of Saturn on August 25, 1981, which gave us breathtaking views of the planet's rings and mysterious moon Titan.h.
Neptune and Uranus Encounters:
Voyager 2 was put on an extraordinary course to travel to Uranus and Neptune after its successful flights to Jupiter and Saturn. Voyager 2's near encounter with Uranus on January 24, 1986, allowed it to take detailed pictures of the planet's numerous moons and distinctively tilted magnetic field. Then, on August 25, 1989, Voyager 2 made history by becoming the first spacecraft to orbit Neptune. This mission revealed Neptune's stunningly blue atmosphere and produced the first-ever up-close views of its largest moon, Triton.
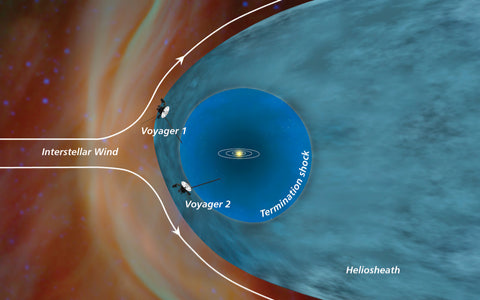
Beyond the Solar System Travel:
Voyager 2 carried out its interstellar voyage after completing its primary planetary missions. It joined Voyager 1 in this historic accomplishment on August 30, 2007, when it crossed the heliosheath, the line denoting the end of the Sun's influence. Both spacecraft are still sending data back to Earth, which is vital for understanding the interstellar medium's characteristics.
Legacy and on-going contributions:
Despite being nearly 40 years old, Voyager 2 is still a symbol of human inventiveness and tenacity. Its outdated equipment are nevertheless providing important information on cosmic rays, magnetic fields, and the far-off heliosphere. The endurance and resiliency of Voyager 2 have motivated subsequent generations of scientists and engineers and continue to raise the bar for deep space exploration.
Conclusion:
The voyage of Voyager 2 is still regarded as a remarkable achievement in the history of space travel. This spacecraft has fundamentally changed our understanding of the solar system and beyond, from its ground-breaking missions to the outer planets to its present investigation of interstellar space. We excitedly await the information it will send back to Earth as it continues its voyage through space, since it will help us solve even more puzzles concerning the vastness of space. The legacy of Voyager 2 will definitely live on, serving as a representation of human curiosity and the desire to explore the cosmos.
.







_poster.jpg)

Post a Comment